In our last Project Management Guide (Planning the Planning – 2) we looked at all the areas of the project we will need to cover in our project planning. Now it is time to get on with it.
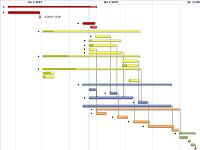
Firstly, I need to make sure we are all on the same page when it comes to what a plan is. Many people (and a distressing number of project managers, too) think only of a Gantt chart when they think of a project plan. You may recognise it as what you get from Microsoft Project. This is better called a project schedule, in that it shows when we expect the various sections of the project to happen. We’ll come back to this later.
What we want to have in our project plan is:
- Aim of project
- Outputs
- Quality criteria
- Resources
- Management structure
- Milestones
- Tolerances
- Dependencies
- Risks
- Schedule
Let’s have a look at these in turn, and see why they are needed, and what we want to achieve with each of them.
Aim of project
What do we want to produce? You’ll recall that we have looked at the reasons for doing the project, and the benefits expected, in Building the Case. (Take a look at the Business Case template (PDF) to refresh your memory.) The aim of the project is a mixture of these. This section of the plan can be either fulfilled by linking to the main Business Case, or by restating it in language for the expected audience. For example, your business case may have been written for high level approval in your organisation. You may want to now put it in terms the project executive expects.
Outputs
Given the aim of the project, what do we actually need to produce to get there? What will your completed project be made up of? These need to be clearly defined. For example, your project’s aim may be to upgrade the IT infrastructure in an organisation. Your final output would be a completed computer network, a new computer on every desk, and all appropriate software installed and ready to go.
Quality criteria
Now we have the outputs, we need to understand what quality they need to be of. In the example above, we have an output of a completed computer network. However, we need to know that the network can actually cope with the amount of traffic going over it!
This means we need the completed output to be of a certain quality, and we need to define what that quality is. These targets tell you what success is, what completion of the project is. They need to be SMART:
- Specific – Clearly defined and precise
- Measurable – e.g. not “new computers”, but “computers with 2Gb of memory”, etc.
- Attainable – Don’t ask for the impossible
- Relevant – Is the criterion actually related to the aim of the project?
- Time-based – Enough time to achieve this. There is no point expecting a year’s worth of work in one week!
It is important you take some time with the stakeholders in your project to produce this list. The final customer of the project will naturally be very involved, but don’t forget your business head – don’t promise everything without considering the costs. Your project executive, and a representative of those who will be doing the work, will have major inputs into this also.
Finally, you will also need to decide who has the final say over the quality of the outputs. Hopefully your work on defining the quality criteria will mean there are no arguments over the quality (i.e. no qualitative judgements, only quantitative) but you need to make sure you schedule in time and people to do the evaluation work.
Resources
We have now set down what outputs we need to produce, and what quality they need to be at. This means we are now in a position to look at the resources we will need to achieve this. Resources include staff time, particular knowledge or skill sets, money (e.g. buying equipment), and time (some tasks can’t be increased by throwing more people at the problem, e.g. delivery times, setting time for concrete, etc.).
Management structure
How are we going to manage the work? You need to describe the general approach to the project here. Who will be the decision makers for the various different streams of work? For example, you may be doing a significant procurement – who makes the decision about what company to buy from?
How will we share progress on the project? Who will we share it to? For example, you may decide to have regular project team meetings – who needs to attend? What level of information will you be sharing? Who else needs to be kept informed, at what level of detail, and how often? For example, you may want to keep the project executive updated at an overview level of detail on a weekly basis, while you keep other managers appraised at a higher level of detail.
You will also need to spell out the relationship of yourself to the project executive, in terms of the monitoring of progress. Equally, you need to put down how you will be monitoring progress of the allocated tasks.
There is no one right answer for how this should be done, and indeed it will vary with every project. Make sure you think about the size and complexity of the project, and also the organisation’s ethos and current management style.
Milestones
Here you need to think about how you will break up the project. Unless it is very small, you don’t want to have the entire project as one lump of work, with the only check on progress at the very end. Instead, it makes sense to break the project up into discrete chunks, where related tasks can be lumped together, with a sensible milestone at the end of them. For example, in the technology refresh in the example above, you may want to break the project down into something like:
- Requirements gathering
- Tender writing
- Tendering process
- Contract negotiation
- Deployment
- Testing
It makes sense to have a defined milestone, so you know when each section is completed. There is also another benefit of breaking the project into chunks, which I’ll come back to.
Tolerances
You will have already looked at the resources you need. Now we need to set how far you, or the project executive, can let the project stray from these targets before needing to sound the alarm. For example, you could set a tolerance in terms of finance of +/- 5%, and a tolerance in terms of time of +/- 10%. Equally, you may want to look at tolerances of quality – i.e. how far from the quality criteria are you willing to accept?
It is remarkably unlikely that a project will not deviate from its resource or quality targets. Setting tolerances allows you to be able to manage the project without continually seeking guidance from the project executive as to whether you should carry on. This is not to say that you should be happy with these deviations, and you should try to avoid them, and monitor them closely. That way you can build your understanding of the project for the future.
Dependencies
This is where you look at what needs to happen before something else. For example, in our example above, you need to complete the requirements gathering before you can finish the tender documentation. You need to start thinking about the dependencies so you, and the project team, can understand the impact of changes in any part of the project.
These dependencies should include both those internal to the project (i.e. those under your control), and those external to it (i.e. those outside of your control). For example, you may need an accurate figure for the number of staff in the organisation. This needs to come from your HR department, and would be an external dependency.
Risks
Simply, what could go wrong? What could happen that would damage your ability to deliver the project? Are there things you can do to avoid them, or minimise them?
Scheduling
This is the Gantt chart-style information that many people envisage when a project plan is mentioned. In this, you need to put down what you expect to happen when. It will include your dependencies, milestones, and probably resources. At this point, it will be a relatively high overview of the whole project.
There is something you need to understand about this schedule, and that is this: it will be wrong.
I know that seems a strong statement, but it is vital that you understand that you cannot make a perfect schedule. You really would be getting into the realm of prophecy if you think you can sit down now, and accurately and precisely pinpoint the date the project will end. No, what you need to do here is achieve the possible.
The schedule needs to include the overview, with the project broken down into sensible chunks. This is the other advantage of breaking the project into chunks we mentioned above. By having the project broken up in this way, you will be able to start planning the first section in quite some detail, extending out for a few weeks. But from then on, it will start to be based more and more on blind guesswork and faith. Don’t try to be artificially precise – keep it vague, use rough figures.
As you come to the end of each chunk of the project, you will be able to plan the next one. You can use the information and experience you have just gained from the previous section, and thus you will be able to be more confident.
Make sure you explain this to your project stakeholders! Often your project executive may look at a schedule, and imagine everything is laid out and known. You must get this idea out of their head straight away! Explain that the early part is firmer than the rest, and make sure they expect changes as the project moves on.
Your boss will crave certainty, and absolute dates for the project, from the very beginning. You must resist the pressure to name a specific date, and explain why. While there may be a temptation to give an answer (no doubt of a date plucked, essentially, from the air) you need to instead be realistic about what is and isn’t possible in terms of scheduling. Anything else can only lead to trouble for you, the project, and ultimately your boss further down the line.
Now we need to do all this!
Phew! That’s a lot to fit into a plan! But don’t worry, you won’t be doing this alone.
You see, you cannot know everything you need to complete the plan, and you shouldn’t expect to. I’ve mentioned bringing other people in to decide what success looks like, and it is vital that you bring people in to help with the scheduling. You will have a project team who will be doing the work, and it is probable, if not certain, that they will have a better idea than you of how to break down a chunk of work into specific tasks, and how long those tasks will take. Make use of their knowledge! This has the added benefit of bringing them into the project, and helping to start the process of turning a group of individuals into a team. In the next section of the Project Management Guide, I’ll be looking at some of the techniques and tips to carry out successful scheduling meetings.
That’s my idea of what is needed in a project plan. What have I missed? Do you include something else? Or do you manage with much less? Comment below and let me know!
 We now have a project management team and structure in place. We’re agreed we want to move ahead with the project idea. We need to put in place what we need to actually carry out the project. In the
We now have a project management team and structure in place. We’re agreed we want to move ahead with the project idea. We need to put in place what we need to actually carry out the project. In the  In our last installment of the project management guide,
In our last installment of the project management guide,